2025-03-18 12:46:59 +08:00
|
|
|
|
# 李雅普诺夫方法
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
判断系统是否能够在受到扰动后返回平衡状态或维持在稳定状态。
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
## 数学基础
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
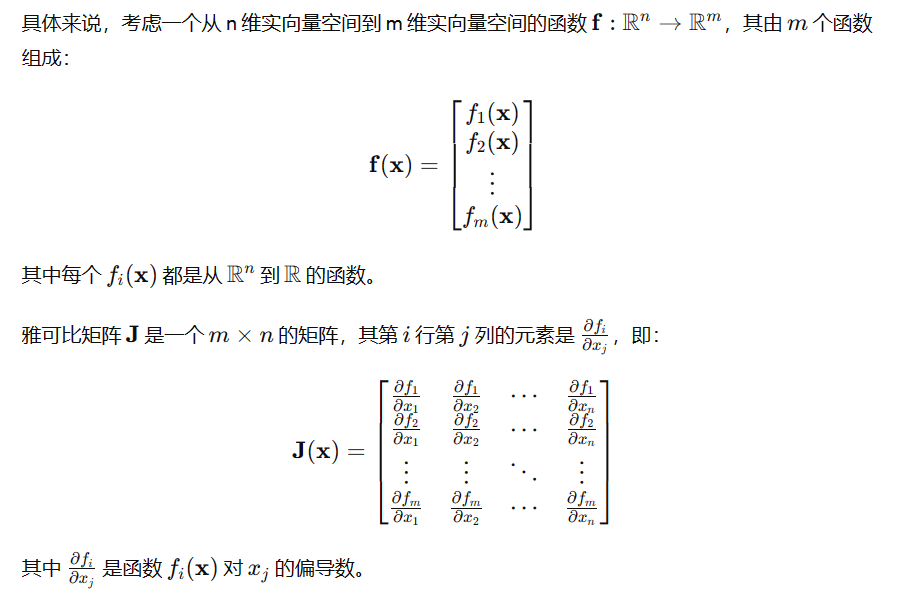
**雅各比矩阵定义**
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
雅可比矩阵(Jacobian matrix)是一个重要的数学概念,它在向量值函数的微分方面起着关键作用。雅可比矩阵描述了一个向量值函数的局部线性近似。
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2025-03-19 18:31:37 +08:00
|
|
|
|
|
2025-03-18 12:46:59 +08:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
理解:从n维实向量空间到m维实向量空间的函数f,假设输入为2维,用x,y表示,即二维平面上的一个点;输出为3维,每个点的位置由坐标f1(x,y),f2(x,y),f3(x,y)表示。
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
**求解雅各比矩阵:**
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2025-03-19 18:31:37 +08:00
|
|
|
|

|
2025-03-18 12:46:59 +08:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
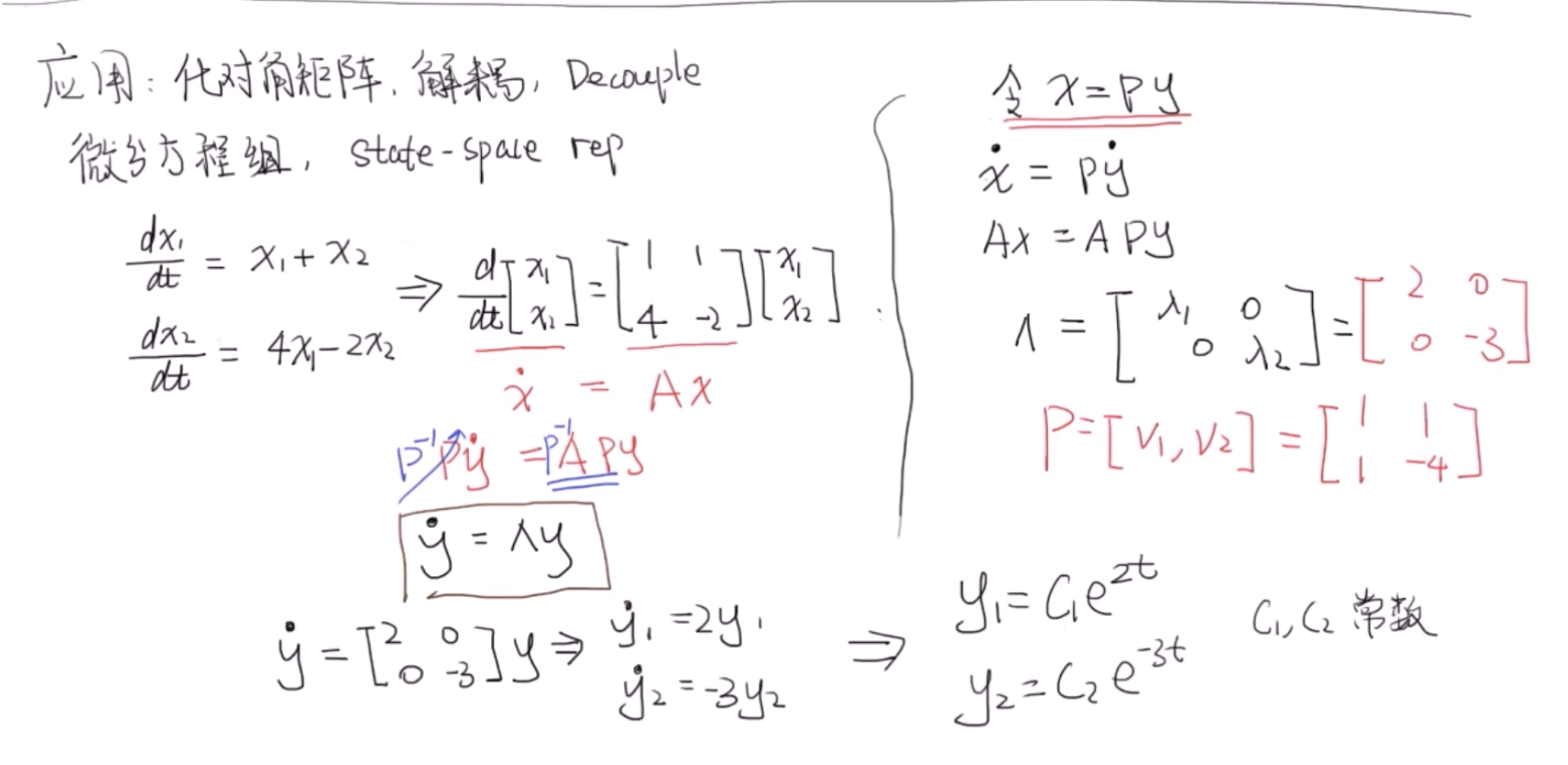
**状态空间**
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2025-03-19 18:31:37 +08:00
|
|
|
|

|
2025-03-18 12:46:59 +08:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
**特征值、特征向量的几何意义**
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2025-03-19 18:31:37 +08:00
|
|
|
|

|
2025-03-18 12:46:59 +08:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
矩阵A表示某线性变换
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2025-03-19 18:31:37 +08:00
|
|
|
|
|
2025-03-18 12:46:59 +08:00
|
|
|
|
|
2025-03-19 18:31:37 +08:00
|
|
|
|
<img src="https://pic.bitday.top/i/2025/03/19/u8matf-2.png" alt="image-20240413165536752" style="zoom:50%;" />
|
2025-03-18 12:46:59 +08:00
|
|
|
|
|
2025-03-19 18:31:37 +08:00
|
|
|
|
<img src="https://pic.bitday.top/i/2025/03/19/u8jxu7-2.png" alt="image-20240413165512450" style="zoom:50%;" />
|
2025-03-18 12:46:59 +08:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
为结论
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
## 稳定性的定义
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2025-03-19 18:31:37 +08:00
|
|
|
|

|
2025-03-18 12:46:59 +08:00
|
|
|
|
|
2025-03-19 18:31:37 +08:00
|
|
|
|

|
2025-03-18 12:46:59 +08:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
## 李雅普诺夫第一法(间接方法)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
通过分析线性系统的系数矩阵的特征值来判断系统的稳定性
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2025-03-19 18:31:37 +08:00
|
|
|
|

|
2025-03-18 12:46:59 +08:00
|
|
|
|
|
2025-03-19 18:31:37 +08:00
|
|
|
|

|
2025-03-18 12:46:59 +08:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
**雅各比矩阵**使我们能够将非线性系统在平衡点附近的行为**近似为线性系统**。通过这种局部线性化,我们可以应用线性系统理论来研究非线性系统的稳定性。
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
特征值的实部决定了系统在这些点附近是趋向平衡点还是远离平衡点。
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- 所有特征值的实部都小于零意味着系统是渐进稳定的;
|
|
|
|
|
|
- 任何特征值的实部大于零意味着系统在该点是不稳定的。
|
|
|
|
|
|
- 如果所有特征值的实部都不大于零,并且存在实部正好为零的特征值,李一法失效。
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
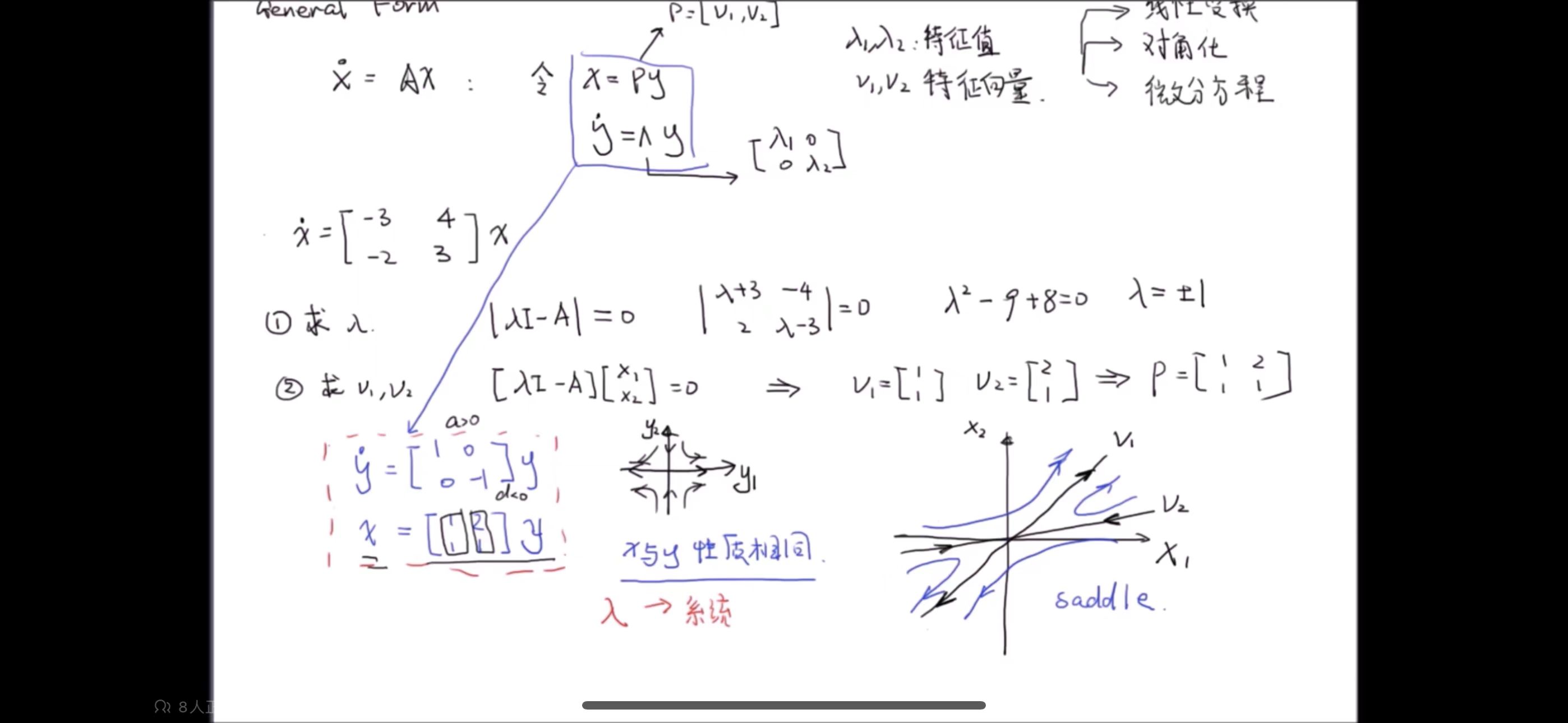
**why特征值???**
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2025-03-19 18:31:37 +08:00
|
|
|
|
|
2025-03-18 12:46:59 +08:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
可以以对角矩阵为例,特征值为对角线上元素,设平衡点x1=0,x2=0;
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- **基变换**:将一个向量**左乘特征向量矩阵V**实际上是在将这个向量**从原始坐标系转换到以A的特征向量为基的新坐标系**。在新的坐标系中,原始向量的坐标表示由特征向量矩阵V 决定。
|
|
|
|
|
|
- 原始坐标系:y1、y2, 新坐标系:x1、x2
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
eg:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2025-03-19 18:31:37 +08:00
|
|
|
|

|
2025-03-18 12:46:59 +08:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
## 希尔维斯特判据
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2025-03-19 18:31:37 +08:00
|
|
|
|

|
2025-03-18 12:46:59 +08:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
## 李雅普诺夫第二法(直接法)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
关键是构造一个李雅普诺夫函数V(x)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2025-03-19 18:31:37 +08:00
|
|
|
|

|
2025-03-18 12:46:59 +08:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2025-03-19 18:31:37 +08:00
|
|
|
|
eg:
|
2025-03-18 12:46:59 +08:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
当使用李雅普诺夫的第二方法分析系统稳定性时,直接找到一个合适的李雅普诺夫函数可能很困难。
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
### 线性定常连续系统
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$$
|
|
|
|
|
|
\dot{x} = Ax
|
|
|
|
|
|
$$
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A为系统的状态矩阵,应用**李雅普诺夫方程**可构造李雅普诺夫函数。
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2025-03-19 18:31:37 +08:00
|
|
|
|

|
2025-03-18 12:46:59 +08:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
eg:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2025-03-19 18:31:37 +08:00
|
|
|
|

|
2025-03-18 12:46:59 +08:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
### 非线性系统
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$$
|
|
|
|
|
|
\dot{x} = f(x)
|
|
|
|
|
|
$$
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
**克拉索夫斯基算法**
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2025-03-19 18:31:37 +08:00
|
|
|
|

|
2025-03-18 12:46:59 +08:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
eg:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2025-03-19 18:31:37 +08:00
|
|
|
|

|
2025-03-18 12:46:59 +08:00
|
|
|
|
|
2025-03-19 18:31:37 +08:00
|
|
|
|

|
2025-03-18 12:46:59 +08:00
|
|
|
|
|