403 lines
12 KiB
Markdown
403 lines
12 KiB
Markdown
|
|
## Mybatis
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
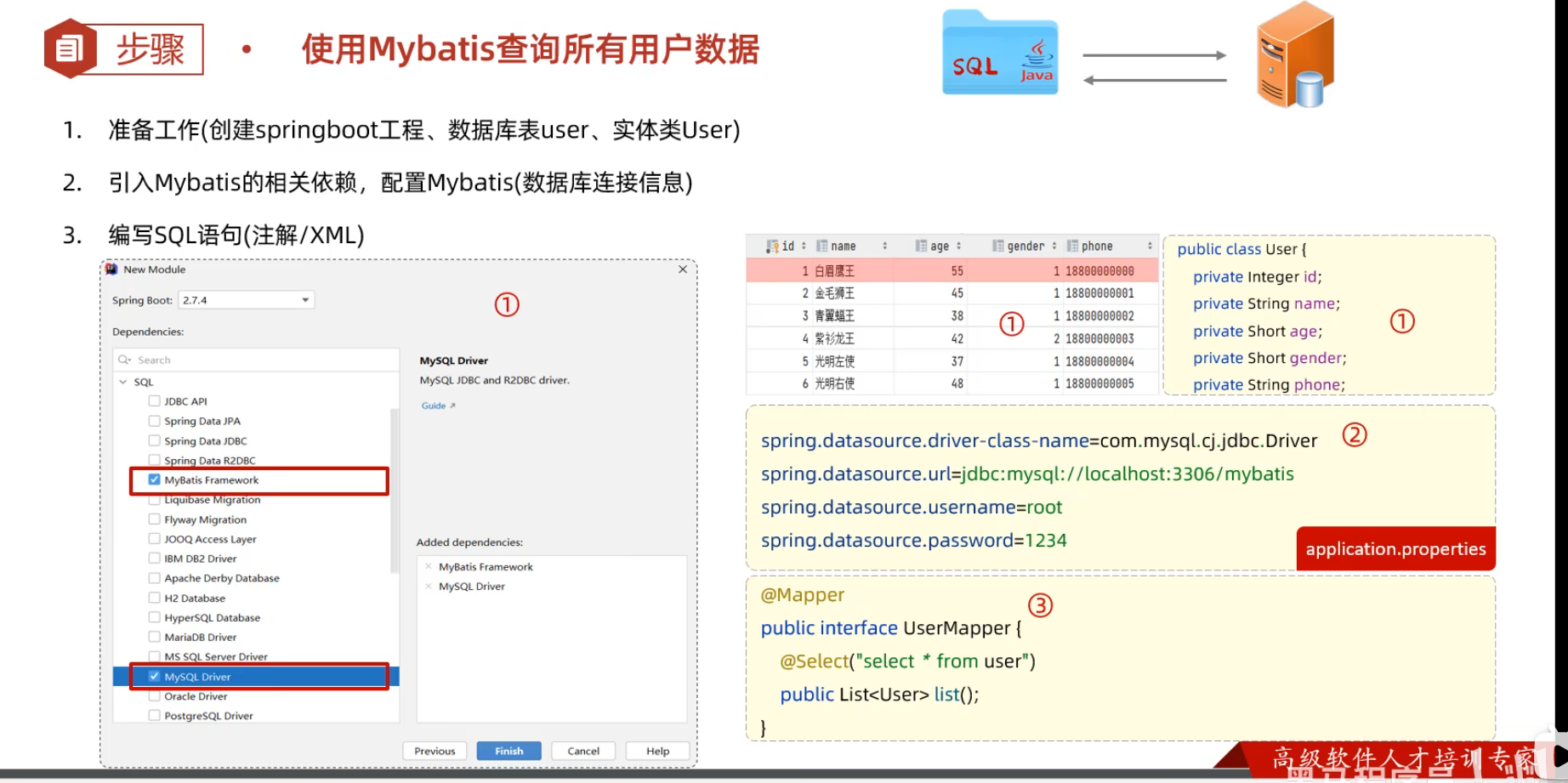
### 快速创建
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
1. 创建springboot工程(Spring Initializr),并导入 mybatis的起步依赖、mysql的驱动包。创建用户表user,并创建对应的实体类User
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
2. 在springboot项目中,可以编写main/resources/application.properties文件,配置数据库连接信息。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
#驱动类名称
|
|||
|
|
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
|
|||
|
|
#数据库连接的url
|
|||
|
|
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis
|
|||
|
|
#连接数据库的用户名
|
|||
|
|
spring.datasource.username=root
|
|||
|
|
#连接数据库的密码
|
|||
|
|
spring.datasource.password=1234
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
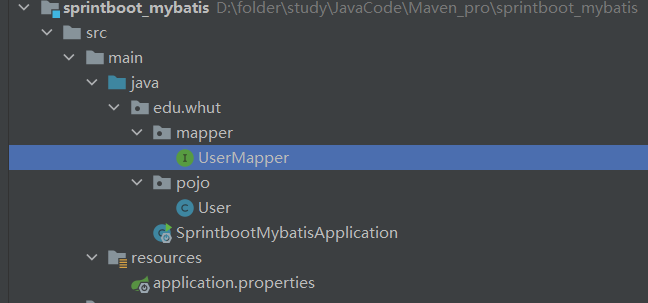
3. 在引导类所在包下,在创建一个包 mapper。在mapper包下创建一个接口 UserMapper
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@Mapper注解:表示是mybatis中的Mapper接口
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
-程序运行时:框架会自动生成接口的**实现类对象(代理对象)**,并交给Spring的IOC容器管理
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@Select注解:代表的就是select查询,用于书写select查询语句
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
```java
|
|||
|
|
@Mapper
|
|||
|
|
public interface UserMapper {
|
|||
|
|
//查询所有用户数据
|
|||
|
|
@Select("select * from user")
|
|||
|
|
public List<User> list();
|
|||
|
|
}
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
### 数据库连接池
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
数据库连接池是一个容器,负责管理和分配数据库连接(`Connection`)。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
- 在程序启动时,连接池会创建一定数量的数据库连接。
|
|||
|
|
- 客户端在执行 SQL 时,从连接池获取连接对象,执行完 SQL 后,将连接归还给连接池,以供其他客户端复用。
|
|||
|
|
- 如果连接对象长时间空闲且超过预设的最大空闲时间,连接池会自动释放该连接。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
**优势**:避免频繁创建和销毁连接,提高数据库访问效率。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Druid(德鲁伊)
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
* Druid连接池是阿里巴巴开源的数据库连接池项目
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
* 功能强大,性能优秀,是Java语言最好的数据库连接池之一
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
把默认的 Hikari 数据库连接池切换为 Druid 数据库连接池:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
1. 在pom.xml文件中引入依赖
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
```xml
|
|||
|
|
<dependency>
|
|||
|
|
<!-- Druid连接池依赖 -->
|
|||
|
|
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
|
|||
|
|
<artifactId>druid-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
|
|||
|
|
<version>1.2.8</version>
|
|||
|
|
</dependency>
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
2. 在application.properties中引入数据库连接配置
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
```properties
|
|||
|
|
spring.datasource.druid.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
|
|||
|
|
spring.datasource.druid.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis
|
|||
|
|
spring.datasource.druid.username=root
|
|||
|
|
spring.datasource.druid.password=123456
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
### SQL注入问题
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
SQL注入:由于没有对用户输入进行充分检查,而SQL又是拼接而成,在用户输入参数时,在参数中添加一些SQL关键字,达到改变SQL运行结果的目的,也可以完成恶意攻击。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
在Mybatis中提供的参数占位符有两种:${...} 、#{...}
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
- #{...}
|
|||
|
|
- 执行SQL时,会将#{…}替换为?,生成预编译SQL,会自动设置参数值
|
|||
|
|
- 使用时机:参数传递,都使用#{…}
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
- ${...}
|
|||
|
|
- 拼接SQL。直接将参数拼接在SQL语句中,**存在SQL注入问题**
|
|||
|
|
- 使用时机:如果对表名、列表进行动态设置时使用
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
### 日志输出
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
只建议开发环境使用:在Mybatis当中我们可以借助日志,查看到sql语句的执行、执行传递的参数以及执行结果
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
1. 打开application.properties文件
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
2. 开启mybatis的日志,并指定输出到控制台
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
```java
|
|||
|
|
#指定mybatis输出日志的位置, 输出控制台
|
|||
|
|
mybatis.configuration.log-impl=org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
### 驼峰命名法
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
在 Java 项目中,数据库表字段名一般使用 **下划线命名法**(snake_case),而 Java 中的变量名使用 **驼峰命名法**(camelCase)。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
- [x] **小驼峰命名(lowerCamelCase)**:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
- 第一个单词的首字母小写,后续单词的首字母大写。
|
|||
|
|
- **例子**:`firstName`, `userName`, `myVariable`
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
**大驼峰命名(UpperCamelCase)**:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
- 每个单词的首字母都大写,通常用于类名或类型名。
|
|||
|
|
- **例子**:`MyClass`, `EmployeeData`, `OrderDetails`
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
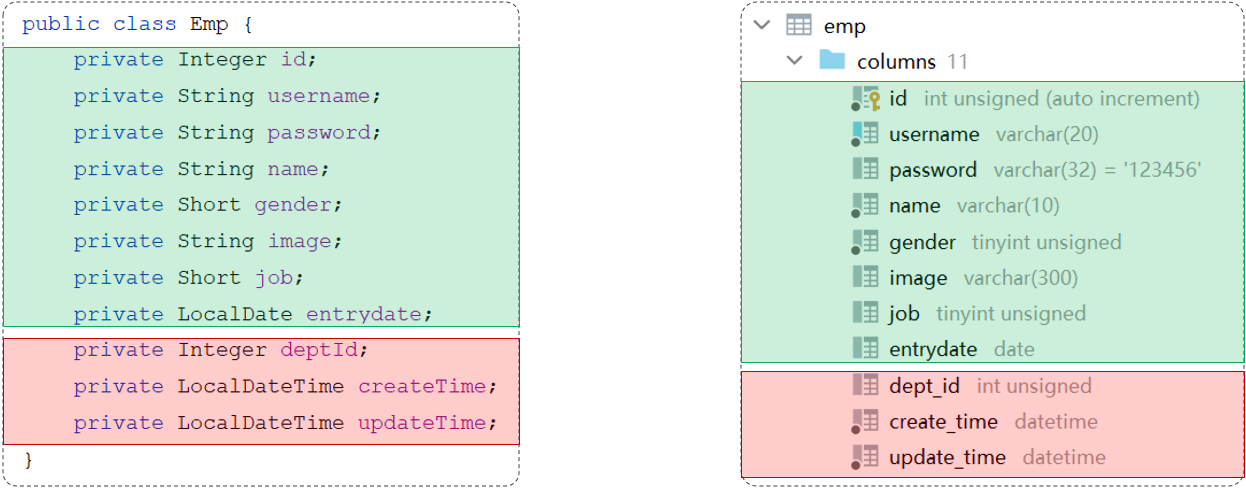
表中查询的数据封装到实体类中
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
- 实体类属性名和数据库表查询返回的**字段名一致**,mybatis会自动封装。
|
|||
|
|
- 如果实体类属性名和数据库表查询返回的字段名不一致,不能自动封装。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
解决方法:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
1. 起别名
|
|||
|
|
2. 结果映射
|
|||
|
|
3. **开启驼峰命名**
|
|||
|
|
4. **属性名和表中字段名保持一致**
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
**开启驼峰命名(推荐)**:如果字段名与属性名符合驼峰命名规则,mybatis会自动通过驼峰命名规则映射
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
> 驼峰命名规则: abc_xyz => abcXyz
|
|||
|
|
>
|
|||
|
|
> - 表中字段名:abc_xyz
|
|||
|
|
> - 类中属性名:abcXyz
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
### 推荐的完整配置:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
```yaml
|
|||
|
|
mybatis:
|
|||
|
|
#mapper配置文件
|
|||
|
|
mapper-locations: classpath:mapper/*.xml
|
|||
|
|
type-aliases-package: com.sky.entity
|
|||
|
|
configuration:
|
|||
|
|
#开启驼峰命名
|
|||
|
|
map-underscore-to-camel-case: true
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
`type-aliases-package: com.sky.entity`把 `com.sky.entity` 包下的所有类都当作别名注册,XML 里就可以直接写 `<resultType="Dish">` 而不用写全限定名。可以多添加几个包,用逗号隔开。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
### 增删改
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
- **增删改通用!:返回值为int时,表示影响的记录数,一般不需要可以设置为void!**
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
**作用于单个字段**
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
```java
|
|||
|
|
@Mapper
|
|||
|
|
public interface EmpMapper {
|
|||
|
|
//SQL语句中的id值不能写成固定数值,需要变为动态的数值
|
|||
|
|
//解决方案:在delete方法中添加一个参数(用户id),将方法中的参数,传给SQL语句
|
|||
|
|
/**
|
|||
|
|
* 根据id删除数据
|
|||
|
|
* @param id 用户id
|
|||
|
|
*/
|
|||
|
|
@Delete("delete from emp where id = #{id}")//使用#{key}方式获取方法中的参数值
|
|||
|
|
public void delete(Integer id);
|
|||
|
|
}
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|

|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
上图参数值分离,有效防止SQL注入
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
**作用于多个字段**
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
```java
|
|||
|
|
@Mapper
|
|||
|
|
public interface EmpMapper {
|
|||
|
|
//会自动将生成的主键值,赋值给emp对象的id属性
|
|||
|
|
@Options(useGeneratedKeys = true,keyProperty = "id")
|
|||
|
|
@Insert("insert into emp(username, name, gender, image, job, entrydate, dept_id, create_time, update_time) values (#{username}, #{name}, #{gender}, #{image}, #{job}, #{entrydate}, #{deptId}, #{createTime}, #{updateTime})")
|
|||
|
|
public void insert(Emp emp);
|
|||
|
|
}
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
在 **`@Insert`** 注解中使用 `#{}` 来引用 `Emp` 对象的属性,MyBatis 会自动从 `Emp` 对象中提取相应的字段并绑定到 SQL 语句中的占位符。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
`@Options(useGeneratedKeys = true, keyProperty = "id")` 这行配置表示,插入时自动生成的主键会赋值给 `Emp` 对象的 `id` 属性。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
// 调用 mapper 执行插入操作
|
|||
|
|
empMapper.insert(emp);
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
// 现在 emp 对象的 id 属性会被自动设置为数据库生成的主键值
|
|||
|
|
System.out.println("Generated ID: " + emp.getId());
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
### 查
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
查询案例:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
- **姓名:要求支持模糊匹配**
|
|||
|
|
- 性别:要求精确匹配
|
|||
|
|
- 入职时间:要求进行范围查询
|
|||
|
|
- 根据最后修改时间进行降序排序
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
重点在于模糊查询时where name like '%#{name}%' 会报错。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
解决方案:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
使用MySQL提供的字符串拼接函数:`concat('%' , '关键字' , '%')`
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
**`CONCAT()`** 如果其中任何一个参数为 **`NULL`**,`CONCAT()` 返回 **`NULL`**,`Like NULL`会导致查询不到任何结果!
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
`NULL`和`''`是完全不同的
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
```java
|
|||
|
|
@Mapper
|
|||
|
|
public interface EmpMapper {
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@Select("select * from emp " +
|
|||
|
|
"where name like concat('%',#{name},'%') " +
|
|||
|
|
"and gender = #{gender} " +
|
|||
|
|
"and entrydate between #{begin} and #{end} " +
|
|||
|
|
"order by update_time desc")
|
|||
|
|
public List<Emp> list(String name, Short gender, LocalDate begin, LocalDate end);
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
}
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
### XML配置文件规范
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
使用Mybatis的注解方式,主要是来完成一些简单的增删改查功能。如果需要实现复杂的SQL功能,建议使用XML来配置映射语句,也就是将SQL语句写在XML配置文件中。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
在Mybatis中使用XML映射文件方式开发,需要符合一定的规范:
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
1. XML映射**文件的名称**与Mapper**接口名称**一致,并且将XML映射文件和Mapper接口放置在相同包下(同包同名)
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
2. XML映射文件的**namespace属性**为Mapper接口**全限定名**一致
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
3. XML映射文件中sql语句的**id**与Mapper接口中的**方法名**一致,并保持返回类型一致。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
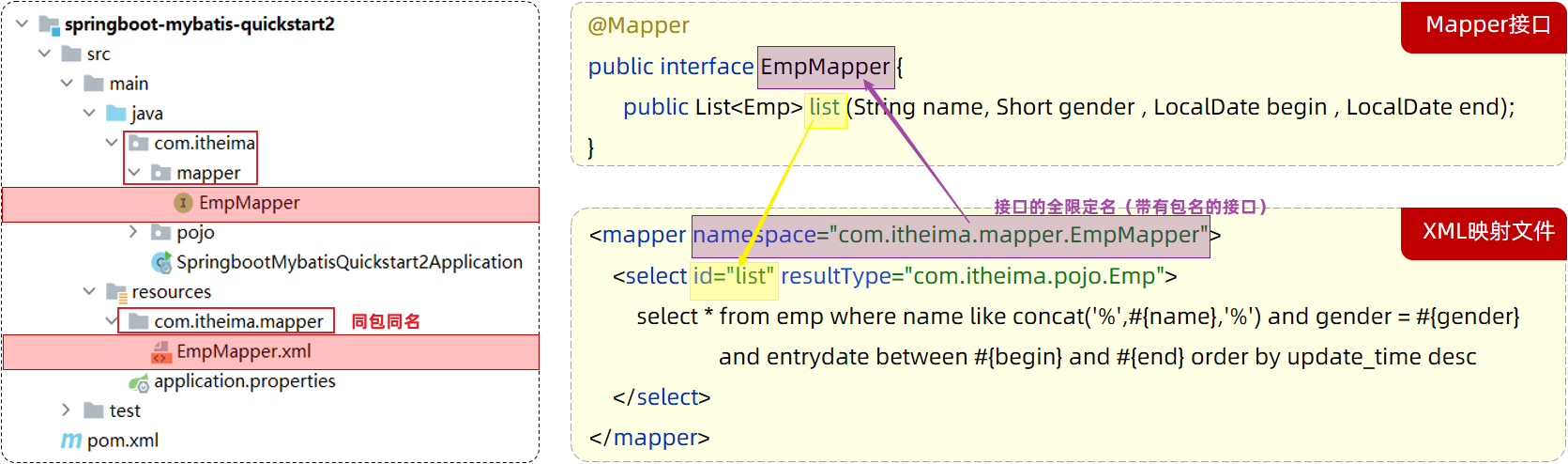
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
\<select>标签:就是用于编写select查询语句的。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
resultType属性,指的是查询返回的单条记录所封装的类型(查询必须)。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
parameterType属性(可选,MyBatis 会根据接口方法的入参类型(比如 `Dish` 或 `DishPageQueryDTO`)自动推断),POJO作为入参,需要使用全类名或是`type‑aliases‑package: com.sky.entity` 下注册的别名。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
<insert id="insert" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id">
|
|||
|
|
<select id="pageQuery" resultType="com.sky.vo.DishVO">
|
|||
|
|
<select id="list" resultType="com.sky.entity.Dish" parameterType="com.sky.entity.Dish">
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
**实现过程:**
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
1. resources下创与java下一样的包,即edu/whut/mapper,新建xx.xml文件
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
2. 配置Mapper文件
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
```xml
|
|||
|
|
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
|
|||
|
|
<!DOCTYPE mapper
|
|||
|
|
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
|
|||
|
|
"https://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
|
|||
|
|
<mapper namespace="edu.whut.mapper.EmpMapper">
|
|||
|
|
<!-- SQL 查询语句写在这里 -->
|
|||
|
|
</mapper>
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
`namespace` 属性指定了 **Mapper 接口的全限定名**(即包名 + 类名)。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
3. 编写查询语句
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
```xml
|
|||
|
|
<select id="list" resultType="edu.whut.pojo.Emp">
|
|||
|
|
select * from emp
|
|||
|
|
where name like concat('%',#{name},'%')
|
|||
|
|
and gender = #{gender}
|
|||
|
|
and entrydate between #{begin} and #{end}
|
|||
|
|
order by update_time desc
|
|||
|
|
</select>
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
**`id="list"`**:指定查询方法的名称,应该与 Mapper 接口中的方法名称一致。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
**`resultType="edu.whut.pojo.Emp"`**:`resultType` 只在 **查询操作** 中需要指定。指定查询结果映射的对象类型,这里是 `Emp` 类。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
这里有bug!!!
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
`concat('%',#{name},'%')`这里应该用`<where>` `<if>`标签对name是否为`NULL`或`''`进行判断
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
### 动态SQL
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
#### SQL-if,where
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
`<if>`:用于判断条件是否成立。使用test属性进行条件判断,如果条件为true,则拼接SQL。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
~~~xml
|
|||
|
|
<if test="条件表达式">
|
|||
|
|
要拼接的sql语句
|
|||
|
|
</if>
|
|||
|
|
~~~
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
`<where>`只会在子元素有内容的情况下才插入where子句,而且会自动去除子句的开头的AND或OR,**加了总比不加好**
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
```java
|
|||
|
|
<select id="list" resultType="com.itheima.pojo.Emp">
|
|||
|
|
select * from emp
|
|||
|
|
<where>
|
|||
|
|
<!-- if做为where标签的子元素 -->
|
|||
|
|
<if test="name != null">
|
|||
|
|
and name like concat('%',#{name},'%')
|
|||
|
|
</if>
|
|||
|
|
<if test="gender != null">
|
|||
|
|
and gender = #{gender}
|
|||
|
|
</if>
|
|||
|
|
<if test="begin != null and end != null">
|
|||
|
|
and entrydate between #{begin} and #{end}
|
|||
|
|
</if>
|
|||
|
|
</where>
|
|||
|
|
order by update_time desc
|
|||
|
|
</select>
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
#### SQL-foreach
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Mapper 接口
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
```java
|
|||
|
|
@Mapper
|
|||
|
|
public interface EmpMapper {
|
|||
|
|
//批量删除
|
|||
|
|
public void deleteByIds(List<Integer> ids);
|
|||
|
|
}
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
XML 映射文件
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
`<foreach>` 标签用于遍历集合,常用于动态生成 SQL 语句中的 IN 子句、批量插入、批量更新等操作。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
```java
|
|||
|
|
<foreach collection="集合名称" item="集合遍历出来的元素/项" separator="每一次遍历使用的分隔符"
|
|||
|
|
open="遍历开始前拼接的片段" close="遍历结束后拼接的片段">
|
|||
|
|
</foreach>
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
`open="("`:这个属性表示,在*生成的 SQL 语句开始*时添加一个 左括号 `(`。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
`close=")"`:这个属性表示,在生成的 SQL 语句结束时添加一个 右括号 `)`。
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
例:批量删除实现
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
```java
|
|||
|
|
<delete id="deleteByIds">
|
|||
|
|
DELETE FROM emp WHERE id IN
|
|||
|
|
<foreach collection="ids" item="id" separator="," open="(" close=")">
|
|||
|
|
#{id}
|
|||
|
|
</foreach>
|
|||
|
|
</delete>
|
|||
|
|
```
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
实现效果类似:`DELETE FROM emp WHERE id IN (1, 2, 3);`
|