26 KiB
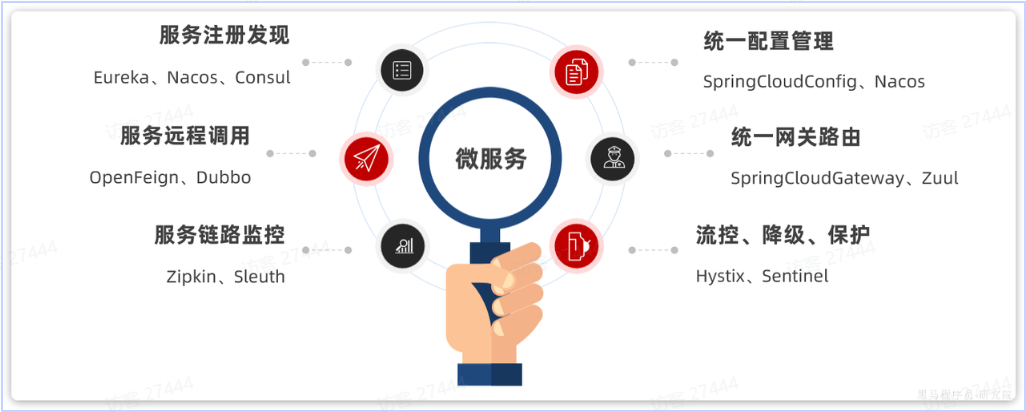
微服务
认识微服务
微服务架构,首先是服务化,就是将单体架构中的功能模块从单体应用中拆分出来,独立部署为多个服务。
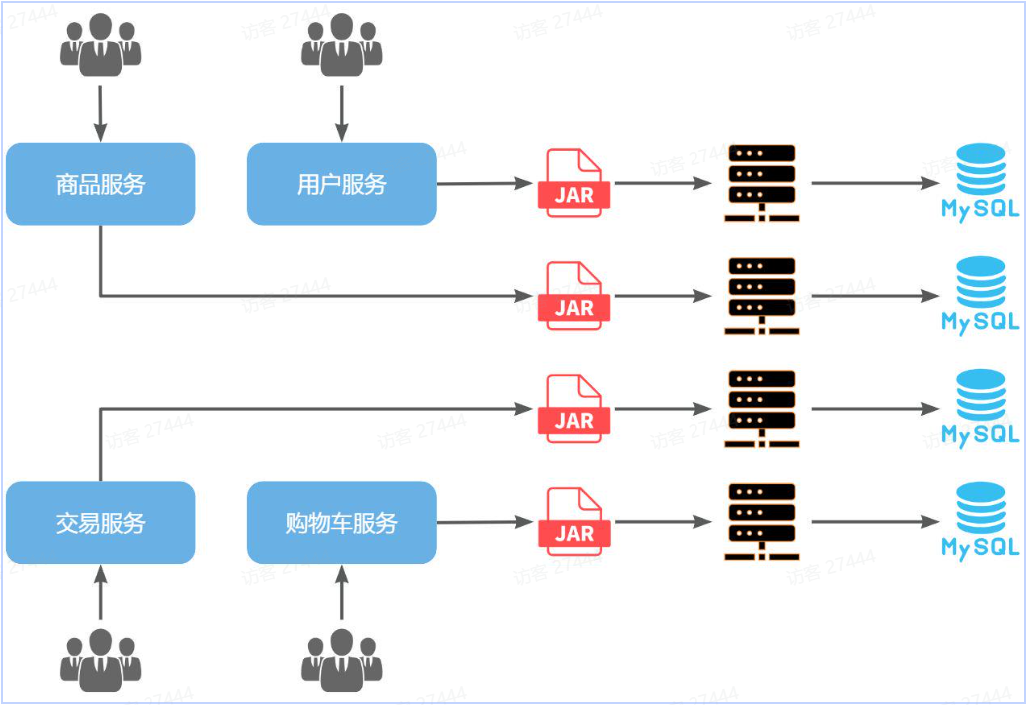
SpringCloud
使用Spring Cloud 2021.0.x以及Spring Boot 2.7.x版本(需要对应)。
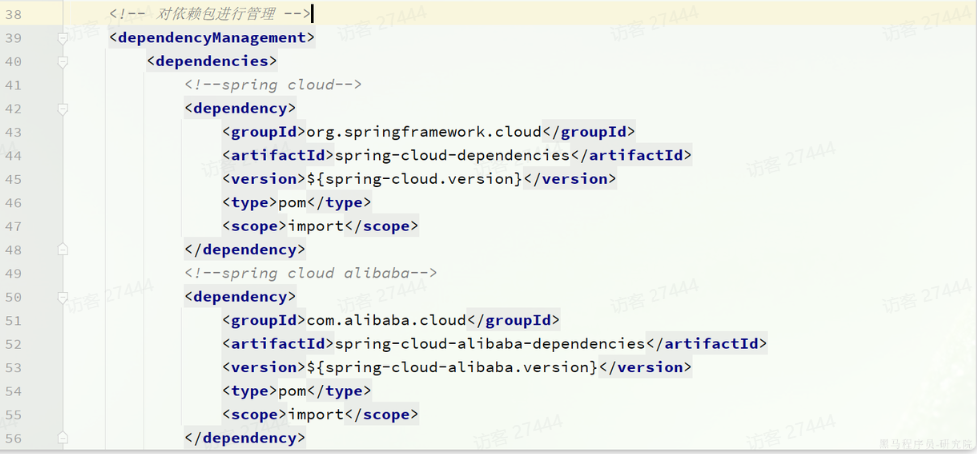
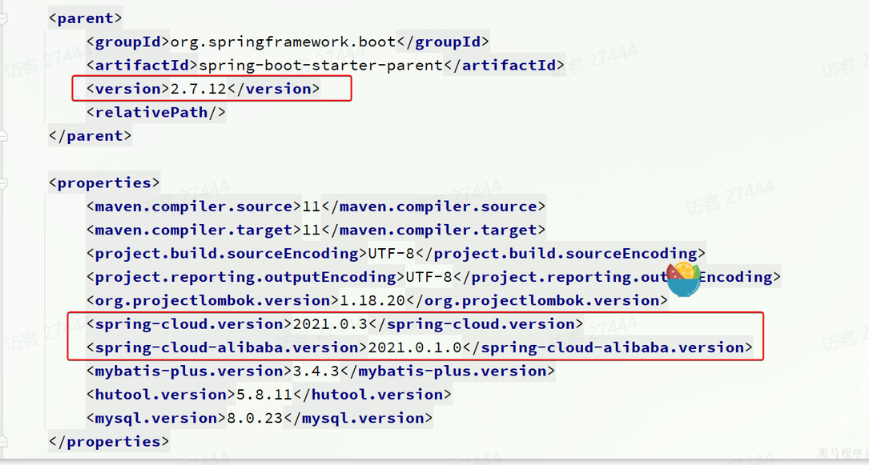
在父pom中的<dependencyManagement>锁定版本,使得后续你在子模块里引用 Spring Cloud 或 Spring Cloud Alibaba 的各个组件时,不需要再写 <version>,Maven 会统一采用你在父 POM 中指定的版本。
微服务拆分
微服务拆分时:
- 高内聚:每个微服务的职责要尽量单一,包含的业务相互关联度高、完整度高。
- 低耦合:每个微服务的功能要相对独立,尽量减少对其它微服务的依赖,或者依赖接口的稳定性要强。
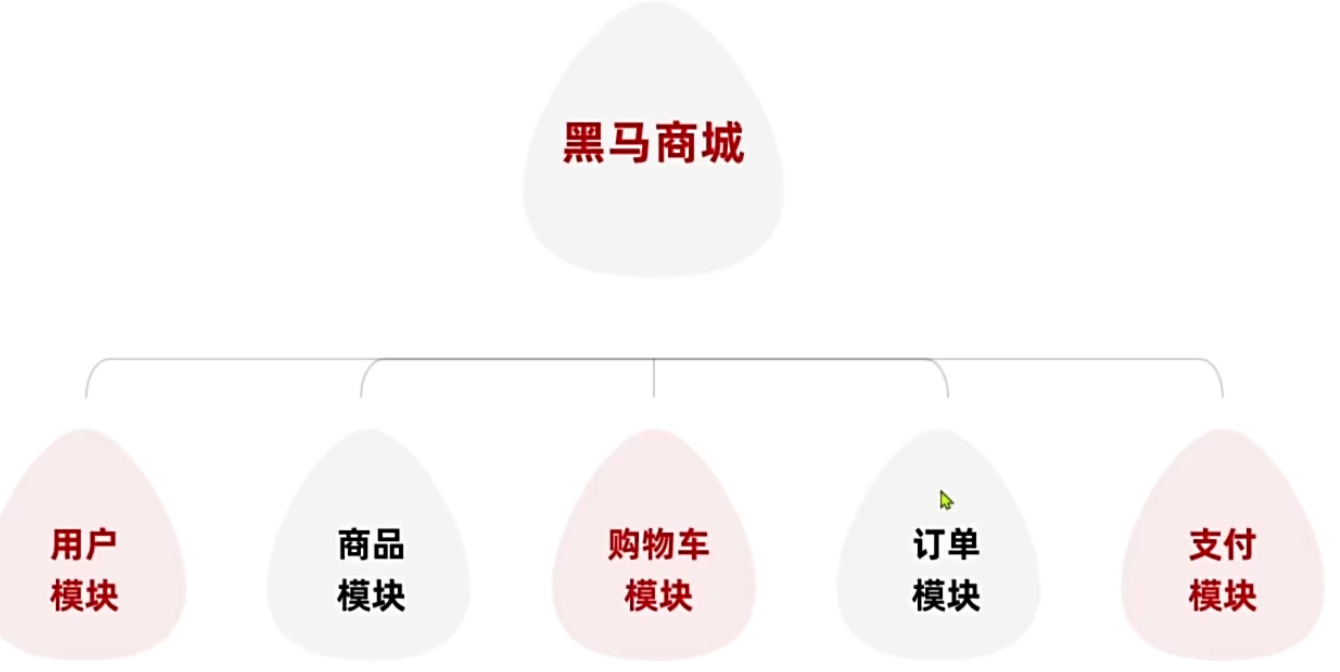
一般微服务项目有两种不同的工程结构:
- 完全解耦:每一个微服务都创建为一个独立的工程,甚至可以使用不同的开发语言来开发,项目完全解耦。
- 优点:服务之间耦合度低
- 缺点:每个项目都有自己的独立仓库,管理起来比较麻烦
- Maven聚合:整个项目为一个Project,然后每个微服务是其中的一个Module
- 优点:项目代码集中,管理和运维方便
- 缺点:服务之间耦合,编译时间较长
,每个模块都要有:pom.xml application.yml controller service mapper pojo 启动类
IDEA配置小技巧:
1.自动导包
2.配置service窗口,以显示多个微服务启动类
3.如何在idea中虚拟多服务负载均衡?
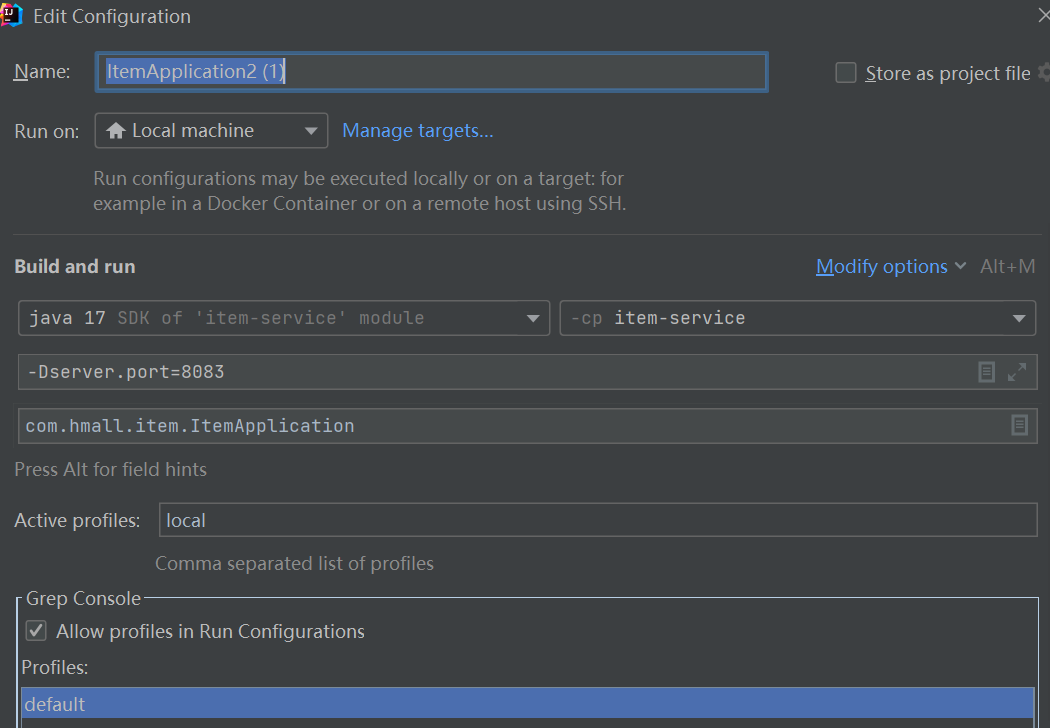
More options->Add VM options -> -Dserver.port=xxxx
这边设置不同的端口号!
服务注册和发现
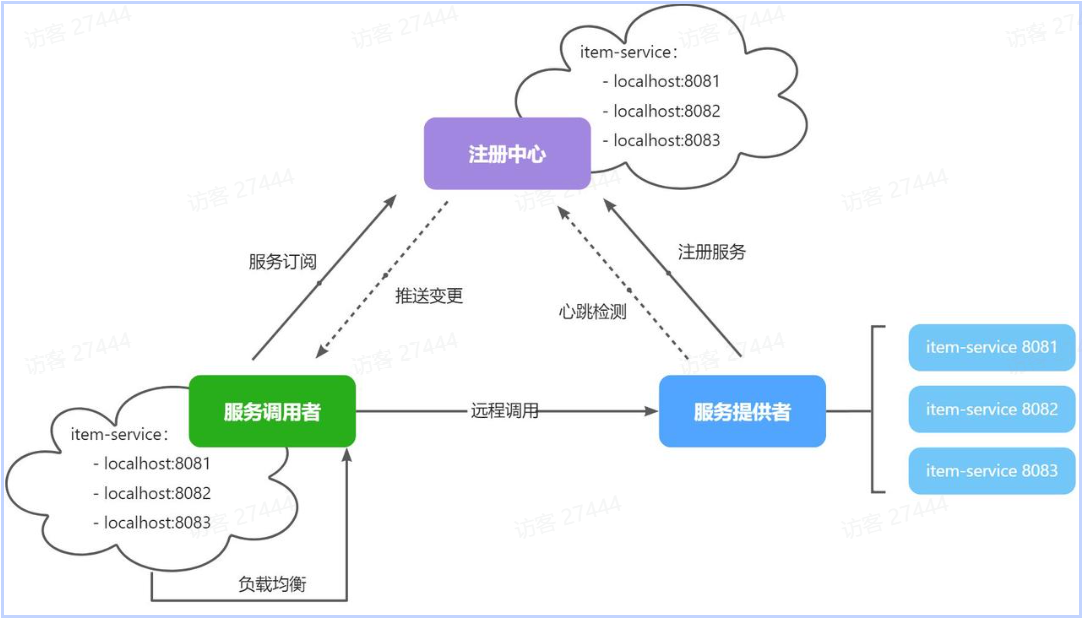
注册中心、服务提供者、服务消费者三者间关系如下:
流程如下:
- 服务启动时就会注册自己的服务信息(服务名、IP、端口)到注册中心
- 调用者可以从注册中心订阅想要的服务,获取服务对应的实例列表(1个服务可能多实例部署)
- 调用者自己对实例列表负载均衡,挑选一个实例
- 调用者向该实例发起远程调用
当服务提供者的实例宕机或者启动新实例时,调用者如何得知呢?
- 服务提供者会定期向注册中心发送请求,报告自己的健康状态(心跳请求)
- 当注册中心长时间收不到提供者的心跳时,会认为该实例宕机,将其从服务的实例列表中剔除
- 当服务有新实例启动时,会发送注册服务请求,其信息会被记录在注册中心的服务实例列表
- 当注册中心服务列表变更时,会主动通知微服务,更新本地服务列表(防止服务调用者继续调用挂逼的服务)
Nacos部署:
1.依赖mysql中的一个数据库 ,可由nacos.sql初始化
2.需要.env文件,配置和数据库的连接信息:
PREFER_HOST_MODE=hostname
MODE=standalone
SPRING_DATASOURCE_PLATFORM=mysql
MYSQL_SERVICE_HOST=124.71.159.***
MYSQL_SERVICE_DB_NAME=nacos
MYSQL_SERVICE_PORT=3307
MYSQL_SERVICE_USER=root
MYSQL_SERVICE_PASSWORD=*******
MYSQL_SERVICE_DB_PARAM=characterEncoding=utf8&connectTimeout=1000&socketTimeout=3000&autoReconnect=true&useSSL=false&allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai
3.docker部署:
nacos:
image: nacos/nacos-server:v2.1.0
container_name: nacos-server
restart: unless-stopped
env_file:
- ./nacos/custom.env # 自定义环境变量文件
ports:
- "8848:8848" # Nacos 控制台端口
- "9848:9848" # RPC 通信端口 (TCP 长连接/心跳)
- "9849:9849" # gRPC 通信端口
networks:
- hm-net
depends_on:
- mysql
volumes:
- ./nacos/init.d:/docker-entrypoint-init.d # 如果需要额外初始化脚本,可选
启动完成后,访问地址:http://ip:8848/nacos/
初始账号密码都是nacos
服务注册
1.在item-service的pom.xml中添加依赖:
<!--nacos 服务注册发现-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-discovery</artifactId>
</dependency>
2.配置Nacos
在item-service的application.yml中添加nacos地址配置:
spring:
application:
name: item-service #服务名
cloud:
nacos:
server-addr: 124.71.159.***:8848 # nacos地址
注意,服务注册默认连9848端口!云服务需要开启该端口!
配置里的item-service就是服务名!
服务发现
前两步同服务注册
3.通过DiscoveryClient发现服务实例列表,然后通过负载均衡算法,选择一个实例去调用
discoveryClient发现服务 + restTemplate远程调用
@Service
public class CartServiceImpl {
@Autowired
private DiscoveryClient discoveryClient; // 注入 DiscoveryClient
@Autowired
private RestTemplate restTemplate; // 用于发 HTTP 请求
private void handleCartItems(List<CartVO> vos) {
// 1. 获取商品 id 列表
Set<Long> itemIds = vos.stream()
.map(CartVO::getItemId)
.collect(Collectors.toSet());
// 2.1. 发现 item-service 服务的实例列表
List<ServiceInstance> instances = discoveryClient.getInstances("item-service");
// 2.2. 负载均衡:随机挑选一个实例
ServiceInstance instance = instances.get(
RandomUtil.randomInt(instances.size())
);
// 2.3. 发送请求,查询商品详情
String url = instance.getUri().toString() + "/items?ids={ids}";
ResponseEntity<List<ItemDTO>> response = restTemplate.exchange(
url,
HttpMethod.GET,
null,
new ParameterizedTypeReference<List<ItemDTO>>() {},
String.join(",", itemIds)
);
// 2.4. 处理结果
if (response.getStatusCode().is2xxSuccessful()) {
List<ItemDTO> items = response.getBody();
// … 后续处理 …
} else {
throw new RuntimeException("查询商品失败: " + response.getStatusCode());
}
}
}
OpenFeign
让远程调用像本地方法调用一样简单
快速入门
1.引入依赖
<!--openFeign-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-openfeign</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--负载均衡器-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-loadbalancer</artifactId>
</dependency>
2.启用OpenFeign
在服务调用者cart-service的CartApplication启动类上添加注解:
@EnableFeignClients
3.编写OpenFeign客户端
在cart-service中,定义一个新的接口,编写Feign客户端:
@FeignClient("item-service")
public interface ItemClient {
@GetMapping("/items")
List<ItemDTO> queryItemByIds(@RequestParam("ids") Collection<Long> ids);
}
queryItemByIds这个方法名可以随便取,但@GetMapping("/items") 和 @RequestParam("ids") 要跟 item-service 服务中实际暴露的接口路径和参数名保持一致(直接参考服务提供者的Controller层对应方法对应即可);
一个客户端对应一个服务,可以在ItemClient里面写多个方法。
4.使用
List<ItemDTO> items = itemClient.queryItemByIds(Arrays.asList(1L, 2L, 3L));
Feign 会帮你把 ids=[1,2,3] 序列化成一个 HTTP GET 请求,URL 形如:
GET http://item-service/items?ids=1&ids=2&ids=3
连接池
Feign底层发起http请求,依赖于其它的框架。其底层支持的http客户端实现包括:
- HttpURLConnection:默认实现,不支持连接池
- Apache HttpClient :支持连接池
- OKHttp:支持连接池
这里用带有连接池的HttpClient 替换默认的
1.引入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>io.github.openfeign</groupId>
<artifactId>feign-httpclient</artifactId>
</dependency>
2.开启连接池
feign:
httpclient:
enabled: true # 使用 Apache HttpClient(默认关闭)
重启服务,连接池就生效了。
最佳实践
如果拆分了交易微服务(trade-service),它也需要远程调用item-service中的根据id批量查询商品功能。这个需求与cart-service中是一样的。那么会再次定义ItemClient接口导致重复编程。
- 思路1:抽取到微服务之外的公共module,需要调用client就引用该module的坐标。
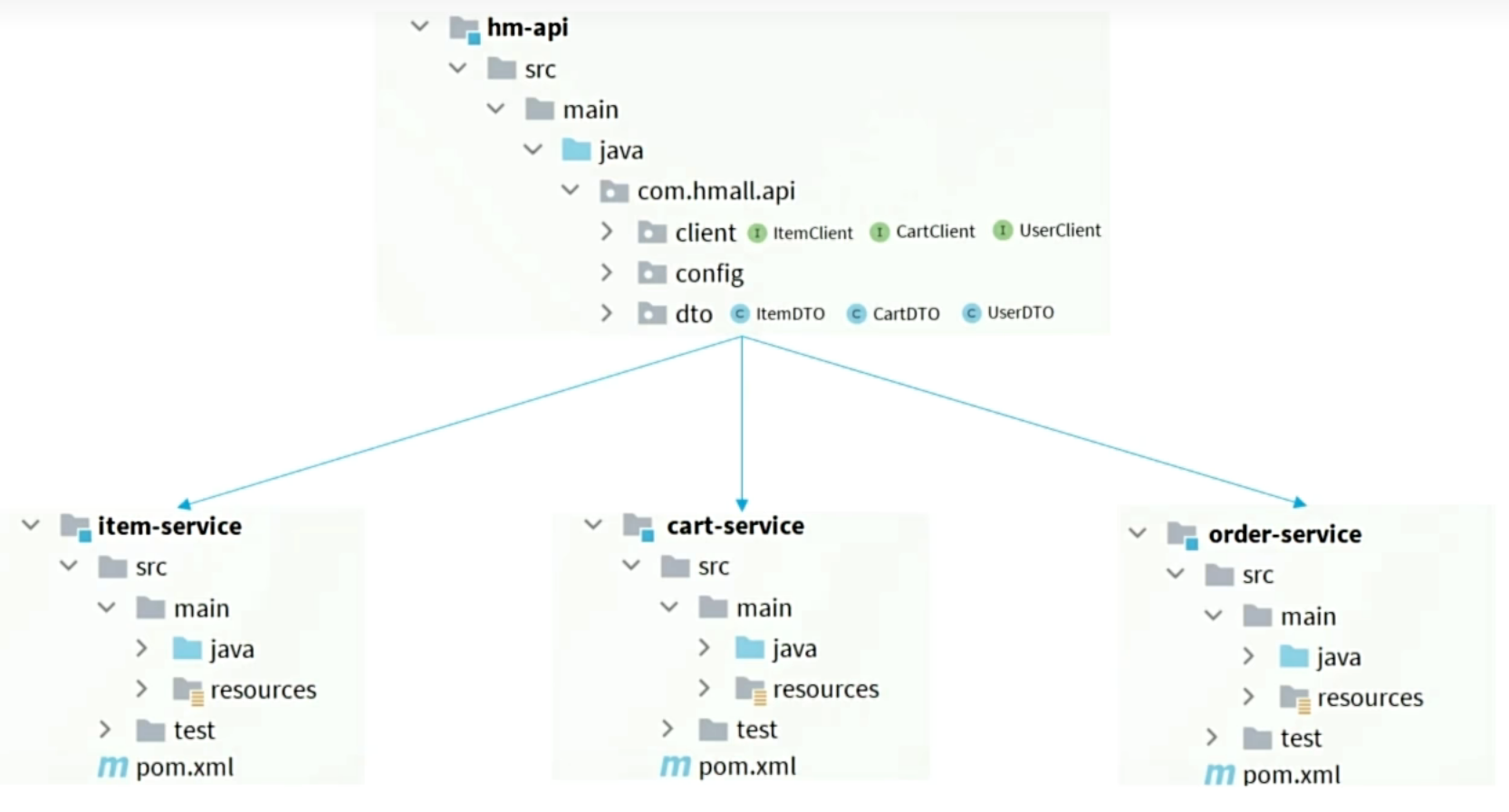
- 思路2:每个微服务自己抽取一个module,比如item-service,将需要共享的domain实体放在item-dto模块,需要供其他微服务调用的cilent放在item-api模块,自己维护自己的,然后其他微服务引入maven坐标直接使用。
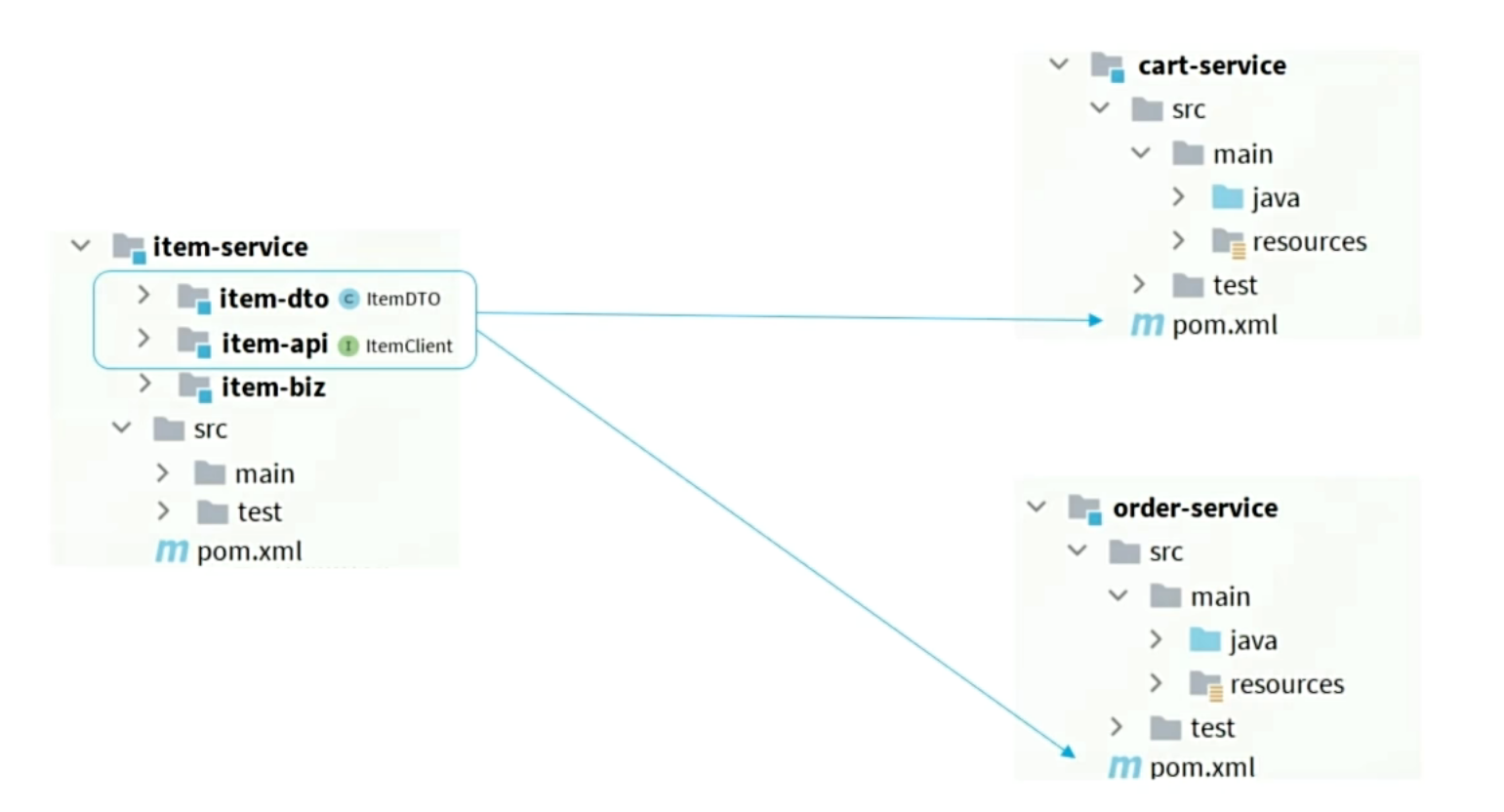
大型项目思路2更清晰、更合理。但这里选择思路1,方便起见。
拆分之后重启报错:Parameter 0 of constructor in com.hmall.cart.service.impl.CartServiceImpl required a bean of type 'com.hmall.api.client.ItemClient' that could not be found.
是因为:Feign Client 没被扫描到,Spring Boot 默认只会在主应用类所在包及其子包里扫描 @FeignClient。
需要额外设置basePackages
package com.hmall.cart;
@MapperScan("com.hmall.cart.mapper")
@EnableFeignClients(basePackages= "com.hmall.api.client")
@SpringBootApplication
public class CartApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(CartApplication.class, args);
}
}
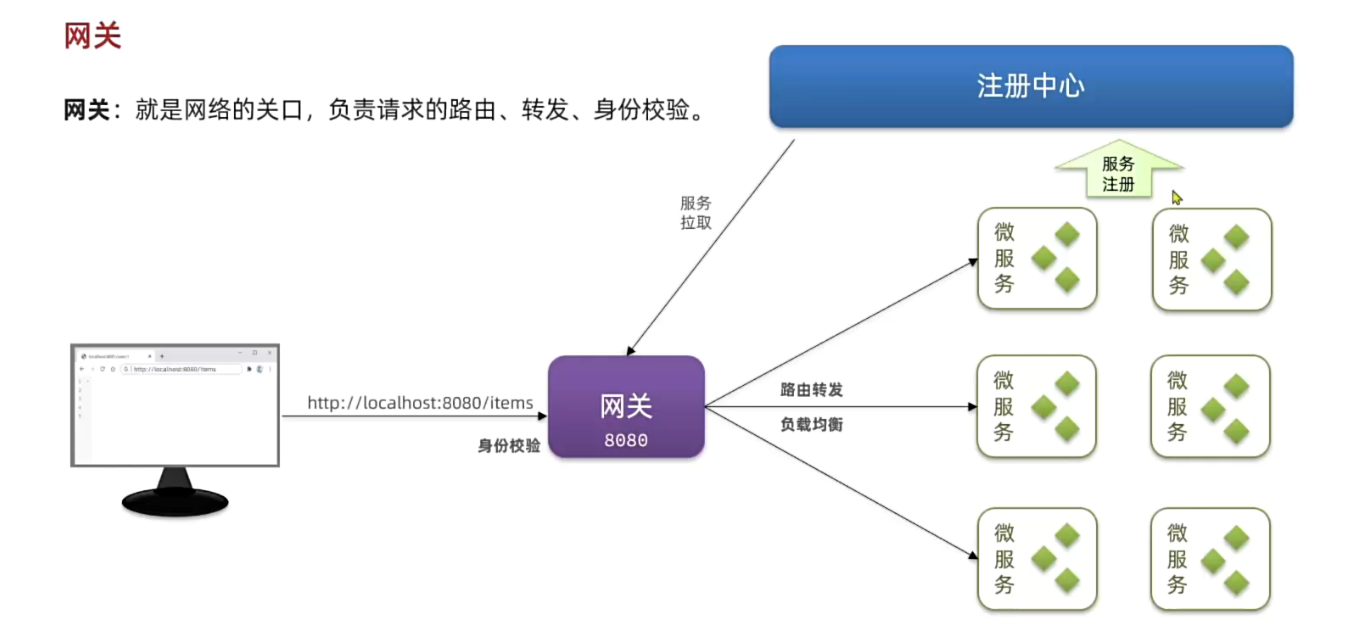
网关
在微服务拆分后的联调过程中,经常会遇到以下问题:
- 不同业务数据分布在各自微服务,需要维护多套地址和端口,调用繁琐且易错;
- 前端无法直接访问注册中心(如 Nacos),无法实时获取服务列表,导致接口切换不灵活。
此外,单体架构下只需完成一次登录与身份校验,所有业务模块即可共享用户信息;但在微服务架构中:
- 每个微服务是否都要重复实现登录校验和用户信息获取?
- 服务间调用时,如何安全、可靠地传递用户身份?
通过引入 API 网关,我们可以在统一入口处解决以上问题:它提供动态路由与负载均衡,前端只需调用一个地址;它与注册中心集成,实时路由调整;它还在网关层集中完成登录鉴权和用户信息透传,下游服务无需重复实现安全逻辑。
快速入门
网关本身也是一个独立的微服务,因此也需要创建一个模块开发功能。大概步骤如下:
- 创建网关微服务
- 引入SpringCloudGateway、NacosDiscovery依赖
- 编写启动类
- 配置网关路由
1.依赖引入:
<!-- 网关 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-gateway</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Nacos Discovery -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-discovery</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- 负载均衡 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-loadbalancer</artifactId>
</dependency>
2.配置网关路由
id:给这条路由起个唯一的标识,方便你在日志、监控里看是哪个规则。(最好和服务名一致)
uri: lb://xxx:xxx 必须和服务注册时的名字一模一样(比如 Item-service 或全大写 ITEM-SERVICE,取决于你在微服务启动时 spring.application.name 配置)
server:
port: 8080
spring:
application:
name: gateway
cloud:
nacos:
server-addr: 192.168.150.101:8848
gateway:
routes:
- id: item # 路由规则id,自定义,唯一
uri: lb://item-service # 路由的目标服务,lb代表负载均衡,会从注册中心拉取服务列表
predicates: # 路由断言,判断当前请求是否符合当前规则,符合则路由到目标服务
- Path=/items/**,/search/** # 支持多个路径模式,用逗号隔开
- id: cart
uri: lb://cart-service
predicates:
- Path=/carts/**
- id: user
uri: lb://user-service
predicates:
- Path=/users/**,/addresses/**
- id: trade
uri: lb://trade-service
predicates:
- Path=/orders/**
- id: pay
uri: lb://pay-service
predicates:
- Path=/pay-orders/**
predicates:路由断言,其实就是匹配条件
| After | 是某个时间点后的请求 | - After=2037-01-20T17:42:47.789-07:00[America/Denver] |
|---|---|---|
| Before | 是某个时间点之前的请求 | - Before=2031-04-13T15:14:47.433+08:00[Asia/Shanghai] |
| Path | 请求路径必须符合指定规则 | - Path=/red/{segment},/blue/** |
Ant风格路径
用来灵活地匹配文件或请求路径:
?:匹配单个字符(除了 /)。
- 例如,
/user/??/profile能匹配/user/ab/profile,但不能匹配/user/a/profile或/user/abc/profile。
*:匹配任意数量的字符(零 个或 多个),但不跨越路径分隔符 /。
- 例如,
/images/*.png能匹配/images/a.png、/images/logo.png,却不匹配/images/icons/logo.png。
**:匹配任意层级的路径(可以跨越多个 /)。
- 例如,
/static/**能匹配/static/、/static/css/style.css、/static/js/lib/foo.js,甚至/static/a/b/c/d。
AntPathMatcher 是 Spring Framework 提供的一个工具类,用来对“Ant 风格”路径模式做匹配
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "auth")
public class AuthProperties {
private List<String> excludePaths;
// getter + setter
}
@Component
public class AuthInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
private final AntPathMatcher pathMatcher = new AntPathMatcher();
private final List<String> exclude;
public AuthInterceptor(AuthProperties props) {
this.exclude = props.getExcludePaths();
}
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest req,
HttpServletResponse res,
Object handler) {
String path = req.getRequestURI(); // e.g. "/search/books/123"
// 检查是否匹配任何一个“放行”模式
for (String pattern : exclude) {
if (pathMatcher.match(pattern, path)) {
return true; // 放行,不做 auth
}
}
// 否则执行认证逻辑
// ...
return false;
}
}
当然
predicates:
- Path=/users/**,/addresses/**
这里不需要手写JAVA逻辑进行路径匹配,因为Gateway自动实现了。但是后面自定义Gateway过滤器的时候就需要AntPathMatcher了!
登录校验
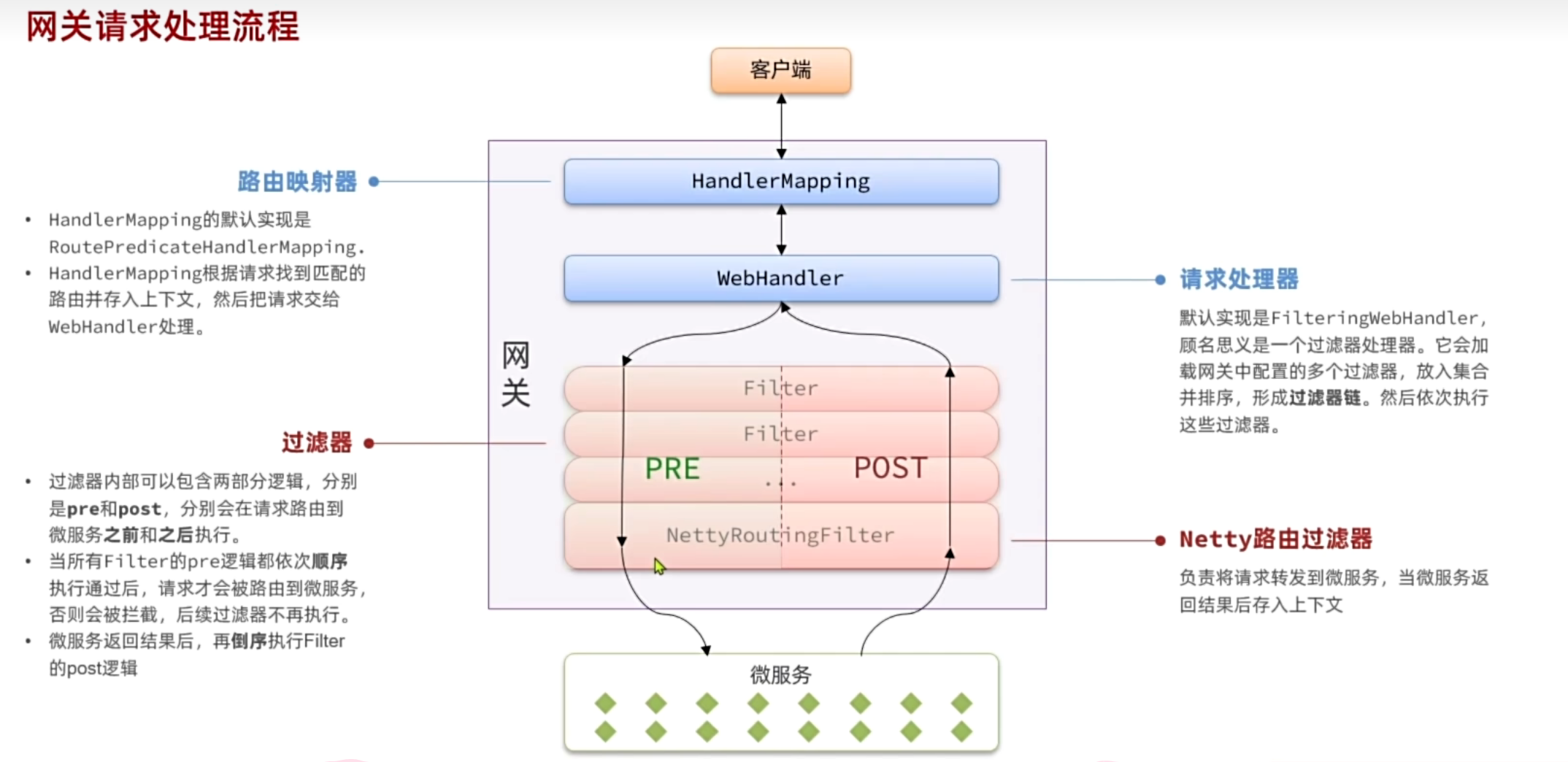
我们需要实现一个网关过滤器,有两种可选:
GatewayFilter:路由过滤器,作用范围比较灵活,可以是任意指定的路由Route.GlobalFilter:全局过滤器,作用范围是所有路由,不可配置。
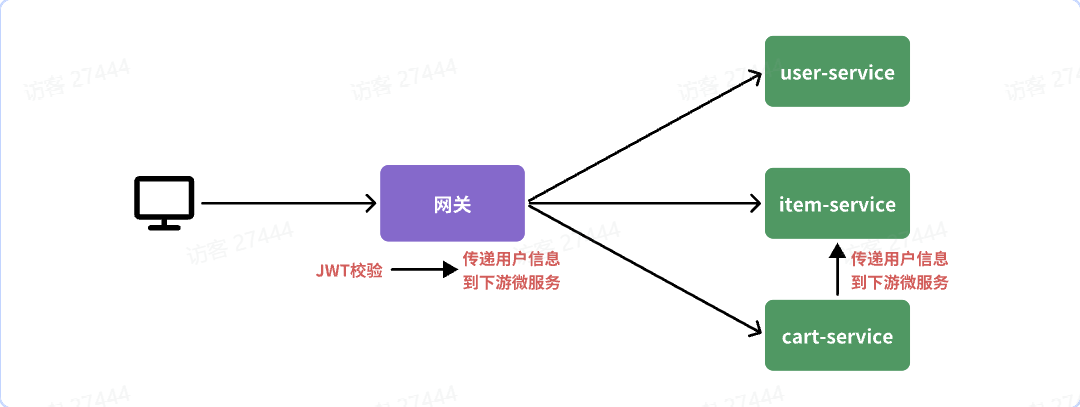
网关需要实现两个功能:1.JWT校验 2.将用户信息传递给微服务
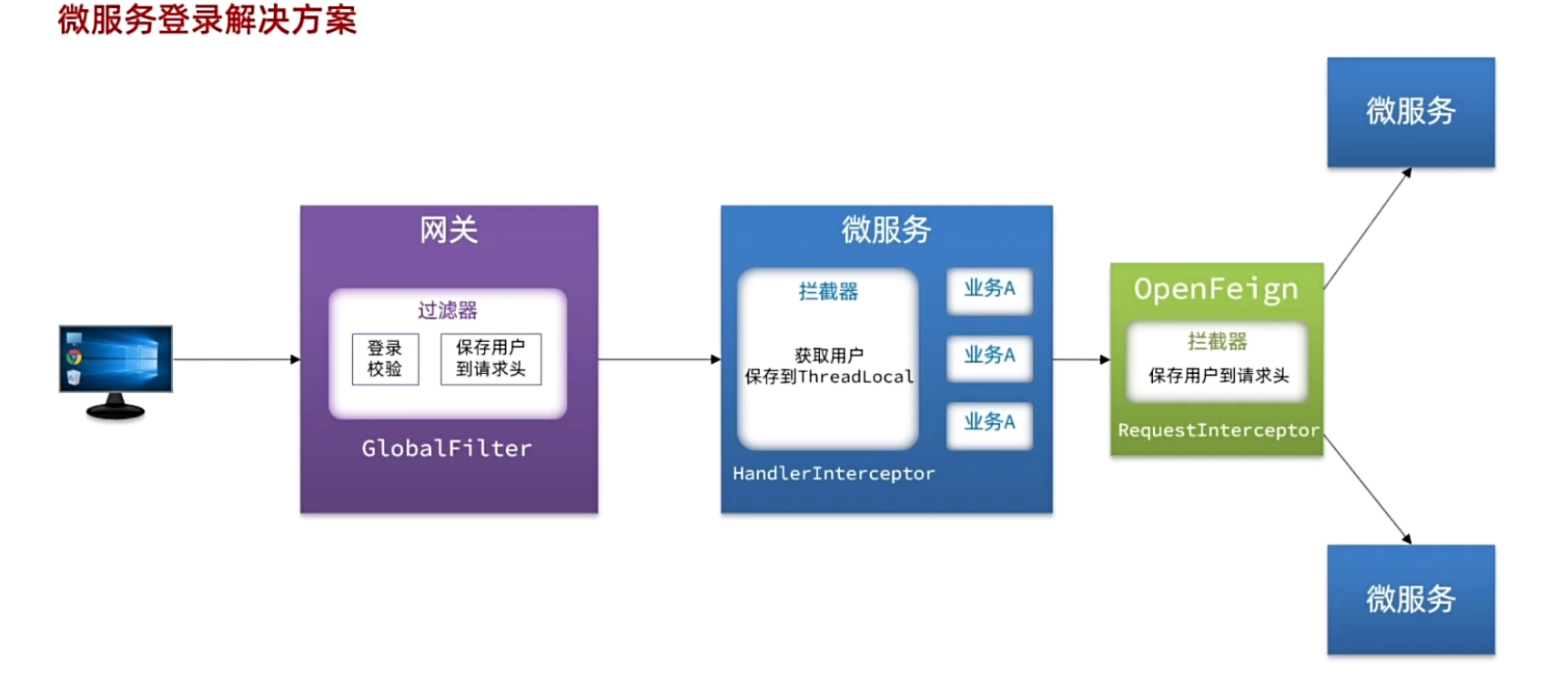
网关校验+存用户信息
@Component
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@EnableConfigurationProperties(AuthProperties.class)
public class AuthGlobalFilter implements GlobalFilter, Ordered {
private final JwtTool jwtTool;
private final AuthProperties authProperties;
private final AntPathMatcher antPathMatcher = new AntPathMatcher();
@Override
public Mono<Void> filter(ServerWebExchange exchange, GatewayFilterChain chain) {
// 1.获取Request
ServerHttpRequest request = exchange.getRequest();
// 2.判断是否不需要拦截
if(isExclude(request.getPath().toString())){
// 无需拦截,直接放行
return chain.filter(exchange);
}
// 3.获取请求头中的token
String token = null;
List<String> headers = request.getHeaders().get("authorization");
if (!CollUtils.isEmpty(headers)) {
token = headers.get(0);
}
// 4.校验并解析token
Long userId = null;
try {
userId = jwtTool.parseToken(token);
} catch (UnauthorizedException e) {
// 如果无效,拦截
ServerHttpResponse response = exchange.getResponse();
response.setRawStatusCode(401);
return response.setComplete();
}
// 5.如果有效,传递用户信息
String userInfo = userId.toString();
ServerWebExchange modifiedExchange = exchange.mutate()
.request(builder -> builder.header("user-info", userInfo))
.build();
// 6.放行
return chain.filter(modifiedExchange);
}
private boolean isExclude(String antPath) {
for (String pathPattern : authProperties.getExcludePaths()) {
if(antPathMatcher.match(pathPattern, antPath)){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
@Override
public int getOrder() {
return 0;
}
}
- 实现
Ordered接口中的getOrder方法,数字越小过滤器执行优先级越高。 exchange可以获得上下文信息。
拦截器获取用户
在Common模块中设置:
只负责保存 userinfo 到 UserContext ,不负责拦截,因为拦截在前面的过滤器做了。
public class UserInfoInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
// 1.获取请求头中的用户信息
String userInfo = request.getHeader("user-info");
// 2.判断是否为空
if (StrUtil.isNotBlank(userInfo)) {
// 不为空,保存到ThreadLocal
UserContext.setUser(Long.valueOf(userInfo));
}
// 3.放行
return true;
}
@Override
public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception {
// 移除用户
UserContext.removeUser();
}
}
配置类:
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnClass(DispatcherServlet.class)
public class MvcConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
registry.addInterceptor(new UserInfoInterceptor());
}
}
注意:Spring Boot 只会从主启动类所在的包(及其子包)去扫描组件。 common 包跟 item、cart 等微服务模块是平级的,无法被扫描到。解决方法:
1.在每个微服务的启动类上添加包扫描
@SpringBootApplication(
scanBasePackages = {"com.hmall.item","com.hmall.common"}
)
主包以及common包
2.在主应用的启动类上用 @Import:
@SpringBootApplication
@Import(com.hmall.common.interceptors.MvcConfig.class)
public class Application { … }
3.前两种方法的问题在于每个微服务模块中都需要写common的引入
因此可以把common 模块做成 Spring Boot 自动配置
1)在common/src/main/resources/META-INF/spring.factories 里声明:
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\
com.hmall.common.config.MvcConfig
2)在 common 模块里给 MvcConfig 加上
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnClass(DispatcherServlet.class) //网关不生效 spring服务生效
public class MvcConfig { … }
3)然后在任何微服务的 pom.xml里只要依赖了这个 common jar,就会自动加载拦截器配置,根本不需要改服务里的 @SpringBootApplication。
OpenFeign传递用户
前端发起的请求都会经过网关再到微服务,微服务可以轻松获取登录用户信息。但是,有些业务是比较复杂的,请求到达微服务后还需要调用其它多个微服务,微服务之间的调用无法传递用户信息,因为不在一个上下文(线程)中!
解决思路:让每一个由OpenFeign发起的请求自动携带登录用户信息。要借助Feign中提供的一个拦截器接口:feign.RequestInterceptor
public class DefaultFeignConfig {
@Bean
public RequestInterceptor userInfoRequestInterceptor(){
return new RequestInterceptor() {
@Override
public void apply(RequestTemplate template) {
// 获取登录用户
Long userId = UserContext.getUser();
if(userId == null) {
// 如果为空则直接跳过
return;
}
// 如果不为空则放入请求头中,传递给下游微服务
template.header("user-info", userId.toString());
}
};
}
}
同时,需要在服务调用者的启动类上添加:
@EnableFeignClients(
basePackages = "com.hmall.api.client",
defaultConfiguration = DefaultFeignConfig.class
)
整体流程图
配置管理
微服务共享的配置可以统一交给Nacos保存和管理,在Nacos控制台修改配置后,Nacos会将配置变更推送给相关的微服务,并且无需重启即可生效,实现配置热更新。
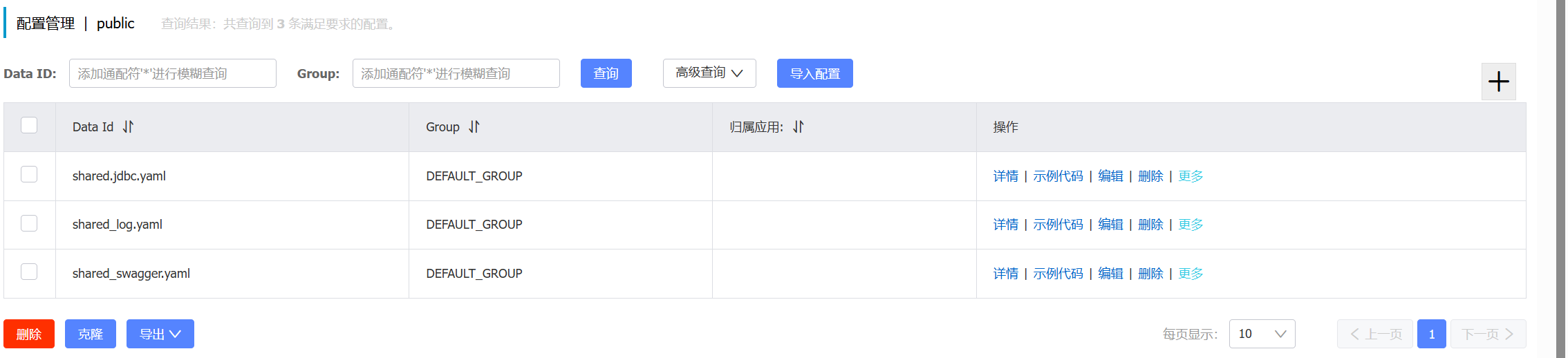
配置共享
在nacos控制台的配置管理中添加配置文件
数据库ip:通过${hm.db.host:192.168.150.101}配置了默认值为192.168.150.101,同时允许通过${hm.db.host}来覆盖默认值
配置读取流程:
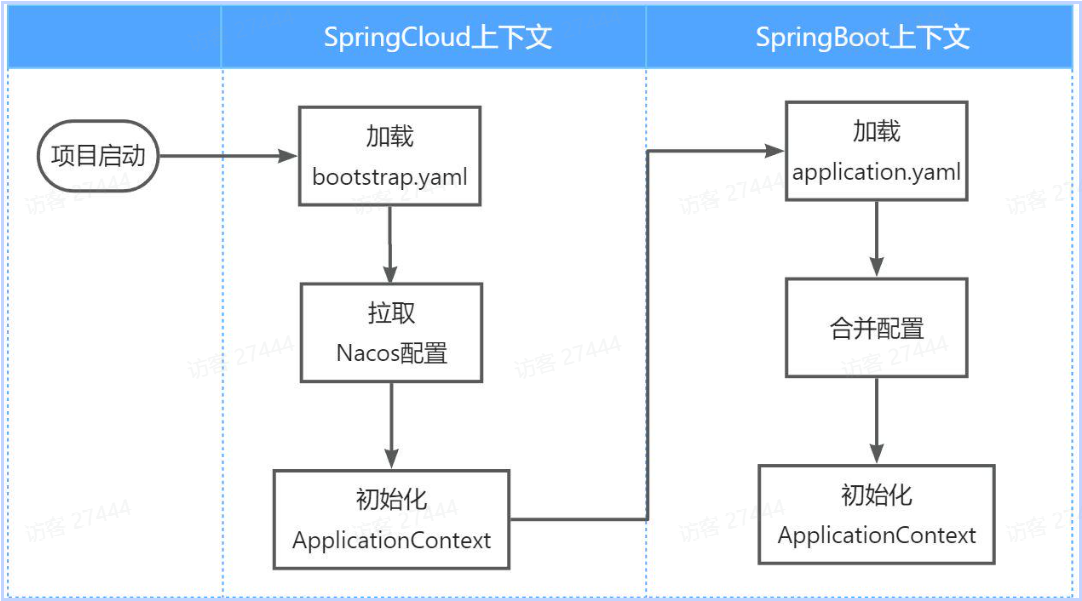
微服务整合Nacos配置管理的步骤如下:
1)引入依赖:
<!--nacos配置管理-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-config</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--读取bootstrap文件-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-bootstrap</artifactId>
</dependency>
2)新建bootstrap.yaml
在cart-service中的resources目录新建一个bootstrap.yaml文件:
主要给nacos的信息
spring:
application:
name: cart-service # 服务名称
profiles:
active: dev
cloud:
nacos:
server-addr: 192.168.150.101 # nacos地址
config:
file-extension: yaml # 文件后缀名
shared-configs: # 共享配置
- dataId: shared-jdbc.yaml # 共享mybatis配置
- dataId: shared-log.yaml # 共享日志配置
- dataId: shared-swagger.yaml # 共享日志配置
3)修改application.yaml
server:
port: 8082
feign:
okhttp:
enabled: true # 开启OKHttp连接池支持
hm:
swagger:
title: 购物车服务接口文档
package: com.hmall.cart.controller
db:
database: hm-cart
配置热更新
有很多的业务相关参数,将来可能会根据实际情况临时调整,如何不重启服务,直接更改配置文件生效呢?
示例:购物车中的商品上限数量需动态调整。
1)在nacos中添加配置
在nacos中添加一个配置文件,将购物车的上限数量添加到配置中:
文件的dataId格式:
[服务名]-[spring.active.profile].[后缀名]
文件名称由三部分组成:
服务名:我们是购物车服务,所以是cart-servicespring.active.profile:就是spring boot中的spring.active.profile,可以省略,则所有profile共享该配置(不管local还是dev还是prod)后缀名:例如yaml
示例:cart-service.yaml
hm:
cart:
maxAmount: 1 # 购物车商品数量上限
2)在微服务中配置
@Data
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "hm.cart")
public class CartProperties {
private Integer maxAmount;
}
下次,只需改nacos中的配置,即可实现热更新。